GRAVITATION NOTES
What will be the effect on the stone? The stone will fly off along a straight line tangential (90 degrees) to the circle at the position of the stone when the stone is released. |
Centripetal force –
- The force acting on any object in a circle and directed towards the centre of the circle is called centripetal force.
- In short, it is centre seeking force. e., due to this force, the object tries to go towards the centre of the circle.
Ex. Motion of moon around the earth.
KEPLER’S LAWS –
Gravitation Notes
Johannes Kepler studied about planetary positions and motions and stated three laws.
Ellipse –
An ellipse is the curve obtained when a cone is cut by an inclined plane. It has 2 foci. The sum of distances of the 2 foci from every point on the curve is constant.
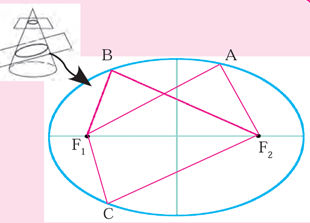
Here, AF1 + AF2 = BF1 + BF2 = CF1 + CF2 = Constant
(When the distance between the planet and the sun is minimum, then the planet moves comparatively faster and when the distance between the planet and the sun is maximum, then the planet moves comparatively slower.)
First law –
The orbit of a planet is an ellipse with the Sun at one of the foci.
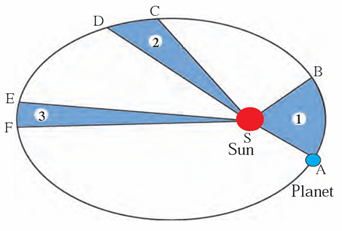
Second law –
The line joining the planet and the Sun sweeps (Covers) equal areas in equal intervals of time.
AB and CD are distances covered by the planet in equal time.
Here, area ASB and CSD are equal.
Third law –
The square of period of revolution of the planet around the Sun is directly proportional to the cube of the mean distance of a planet from the Sun.
Gravitation Notes
If T is the period of revolution of the planet and r is the average distance of planet from the sun.
Then, T2 α r3
i.e., T2 / r3 = constant
Gravitation Notes
If the area ESF in figure 1.4 is equal to area ASB, what will you infer about EF? (Page number 4)According to Kepler’s second law, if area of ESF = area of ASB, then, AB and EF are distances covered by the planet in same time.
|
NEWTON’ SUNIVERSAL LAW OF GRAVITATION –
Every object in the universe attracts every other object with a definite force. This force is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the two objects and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
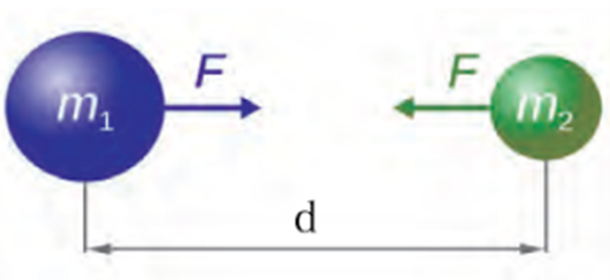
When two objects m1 and m2 are kept at a distance‘d’ from each other,
According to law,
F α m1xm2 ……………. 1
F α 1/d² ……………. 2
Combining 1 & 2
F α m1xm2 / d²
֒ F = Gm1 m2/d2
Here, G is proportionality constant and is called universal gravitation constant.
Gravitational constant:
It is the force of attraction between any two-unit masses separated by a unit distance.
SI unit of G – Nm²/kg²
Its value was calculated by Henry Cavendish as 6.673 ×10 ˉ¹¹Nm²/kg²
UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION
Derivation of inverse square law of gravity with the help of Kepler’s slaw;
When an object moves in a circular path with uniform speed, it has uniform circular motion. If ‘m’ is the mass of the object, v is speed and r is the radius of circle then, the centripetal force acting on it is given as –
F = mv2/r
When a planet is revolving around the sun,
The distance covered by the planet in one revolution=2Πr
R = distance of planet from sun
T = period of revolution
Speed(v) = distance travelled / time taken
= 2Πr / T
We know that, F = mv²/r
֒ F = m (2Πr / T) ²/ r
F =4mΠ²r2 /T²/
__________________
r
F = 4mΠ²r /
T²
By dividing and multiplying by r2
Gravitation notes
F = 4mΠ²r x r2
____________________
T² r2
F = 4mΠ² × r³
________________
r² T²
According to Kepler’s 3rd law, T²/r³ = k
֒ r³/T² = 1/k
֒ F = 4mΠ²
r²k
but, 4mΠ²/k =constant
֒ F = 1/r²
Thus, Newton concluded that the centripetal force acting on the planet must be inversely proportional to the square of distance between planet and the sun.
Gravitation Notes
| Questions on page 7
1. Will the velocity of a stone thrown vertically upwards remain constant or will it change with time? The velocity of the stone thrown vertically upwards decreases with time and at a certain point, it becomes zero. 2. How will it change? Why doesn’t the stone move up all the time? Why does it fall down after reaching a certain height?When a stone is thrown vertically up, it is acted upon by the gravitational force of the earth which pulls the stone down. Due to this, the velocity of the stone becomes zero after reaching a certain height. Once the velocity becomes zero, the object starts moving vertically downwards. 3. What does its maximum height depend on?The maximum height of the stone depends on the initial force on which the initial velocity depends with which the stone is thrown vertically upwards.
|
Gravitation Notes
Eart S Gravitation Notesh’s gravitational force
- The earth attracts every object near it towards itself because of the gravitational force.
- The centre of mass of the earth is situated at its centre, so the gravitational force on any object due to the earth is always directed towards the centre of the earth.
- Because of this force, an object falls vertically downwards on the earth
EARTH’ S GRAVITATIONAL ACCELERATION –
- The gravitational force due to the earth on an object result in its acceleration. This is called acceleration due to gravity or earth’s gravitational acceleration.
OR
- It is the acceleration produced in an object due to gravitational force of the earth
- It is denoted by ‘g’
Think about it (Page 8) –What would happen if there were no gravity?– All the objects will not get attracted to the earth and will float off into space away from the earth. – The moon also will not orbit around the earth. – The important constituents like oceans, atmosphere would also float into space. What would happen if the value of G was twice as large? – The value of acceleration due to gravity (g) would become double. – Weight of all objects would become double and it will become difficult to pick the objects as it would require double force. – The atmospheric air pressure would become double leading to various climatic changes. – Due to rise in atmospheric pressure, the blood pressure would also increase and our survival would become difficult. |
Gravitation Notes
Value of g on the surface of earth –
Suppose, the earth is a sphere of radius R and mass M. Consider an object of mass m is held at a distance r from the centre of the earth.
According to Newton’s law of gravitation, the force of attraction exerted by the earth on the object is –
F = GMm/R2 ……….1
We know that, when an object is falling towards the centre of the earth, its acceleration is due to gravitational force of the earth (g)
According to Newton’s second law of motion, force is the product of mass and acceleration.
F = mg ………2
From equations 1 and 2
mg = GMm/R2
hence, g = GM /R2 ………3
from equation 3, it is clear that, the value of g depends on mass and radius of the earth and it does not depend upon mass of the object
The value of g can be calculated by knowing values of mass of the earth and radius of the earth and G
The mass and radius of the earth are 6 x10 24kg and 6.4×106 m, respectively and value of G = 6.67 x 10-11
g = 6.67 x 10-11 x 6 x10 24
____________________________________
(6.4×106 )2
= 40.02 x 10 24-11
______________________________
40.96 10 12
= 40.02 x 10 13
_____________________________
40.96 10 12
= 0.977 x 10 13 – 12
= 0.977 x 10
= 9.8 m/s2
Gravitation Notes
Can you tell (Page 8) –What would be the value of g on the surface of the earth if its mass was twice as large and its radius half of what it is now?Given –Mass of the earth = M’ = 2M Radius of the earth = R’ = R /2 Find out –Gravitational acceleration (g’) Formula –g = GM / R2 Solution –We know that, g = GM / R2 But here, M = 2M and R = R/2 Therefore, g’ = G2M _______________ (R/2)2 = G x 2M x 4 _______________ R2 = GM x 8 __________________- R2 But, GM / R2 means g. Therefore, g’ = 8 x g = 8 x 9.8 = 78. 4 m/s2 Thus, the value of g would be 8 times its original value.
|
Gravitation Notes
Variation in the value of g
The value of g changes from place to place on the earth. It also varies with the altitude and depth below the earth’s surface. The factors affecting value of g are the shape of the earth, altitude and depth below the earth’s surface.
-
Change along the surface of the earth
- The shape of the earth is not perfectly spherical. It is slightly flat at the poles and bulging at equator.
- Therefore, the radius of the earth at poles is less than the radius at equator.
- Hence, the value of g is highest at the poles (9.832 m/s2) and lowest at the equator. (9.78 m/s2)
-
Height
- As the height of an object from the surface of the earth increases, the distance between the object and the centre of the earth increases.
- As a result, the value of g decreases with increase in height
-
Depth
- The value of g is maximum on the surface of the earth.
- As depth of an object increases, the distance between the object and the centre of the earth decreases.
- Along with the distance, the part of the earth which contributes towards the gravitational force felt by the object (M) also decreases.
- At the center, the mass contributing gravitational force becomes zero. Also the radius becomes zero.
- Thus, due to the combined effect of changing value of radius and mass, the value of g decreases.
- And at the centre it becomes, zero.
Gravitation Notes
MASS AND WEIGHT –
-
Mass –
- It is the amount / quantity of matter present in an object.
- It is represented as m.
- SI unit – Kg
- Mass of an object is always constant. It does not change from place to place.
- It can never be zero.
- It is the measure of inertia of the object.
- It is a scalar quantity. (Has only magnitude and no direction)
-
Weight –
- It is the force with which the object is attracted towards the centre of the earth.
OR
It is the force of earth’s gravity acting on the object.
- It is represented as W
- As force = mass x acceleration, and acceleration is produced by gravitational pull of earth(g)
Therefore, W = F = mg = GMm / R2
- SI unit – Newton (N)
- Weight of an object is not always constant. It changes from place to place. (As value of g changes from place to place)
- It can be zero. (At centre of the earth and interplanetary space)
- It is the measure of gravitational force of the object.
- It is a vector quantity. (Has magnitude and direction)
(Its direction is always towards the centre of the earth.)
Use your brain power –Will your weight remain constant as you go above the surface of the earth?No, our weight will not remain constant if we move away from the surface of the earth. Weight is the product of mass and gravitational acceleration. When we move away from the surface of the earth, mass remains the same but the value of gravitational acceleration decreases. Hence, weight decreases. Suppose you are standing on a tall ladder. If your distance from the centre of the earth is 2R, what will be your weight?
|
Gravitation Notes
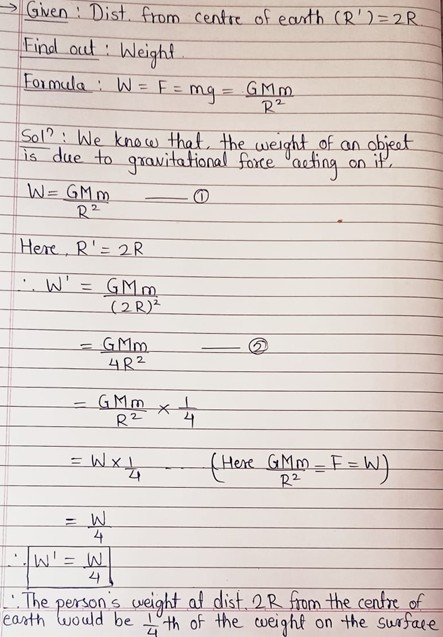
GRAVITATIONAL WAVES –
- These are the ripples in space time caused by some most violent and energetic processes in the Universe.
- Albert Einstein predicted their existence in 1916 in his general theory of relativity.
- Einstein’s theory showed that massive accelerating objects like neutron stars or black holes orbiting each other would disrupt space time such that the waves propagate in all directions away from the source.
- Hence, these waves are called waves on fabric of space time.
- These waves are very weak and difficult to detect.
- Very sensitive instruments like LIGO (Laser Interferometric Gravitational wave Observatory) are used to detect these waves.
FREE FALL
- When an object moves under the influence of the force of gravity alone, it is said to be freely falling.
- In free fall, the initial velocity of the object is zero and goes on increasing due to the acceleration due to gravity of the earth.
- During free fall, the frictional force due to air opposes the motion of the object and a buoyant force also acts on the object.
- Thus, free fall is possible only in vacuum.
- For freely falling body, to calculate its velocity, Newton’s equations become as –
For free fall, u = 0 and a=g
Hence, the three equations of motion become-
V=gt
S=1/2gt2
V2=2gs
(For upward motion, g is negative and for downward motion, it is positive
Gravitational Potential Energy –
- The energy possessed by an object because of its position in gravitational field.
- This energy increases as we go to greater heights from earth surface.
- For object at infinite distance from the earth, the value of g is zero so, the value of potential energy is zero.
- For smaller distances, potential energy is less than zero. (-ve)
- For an object at height h from earth surface, Potential energy is -GMm/R+h
Escape velocity –
- It is the minimum initial velocity needed for an object to escape from the gravitational influence of the earth.
OR
When a body is thrown vertically upward, it is given the minimum initial velocity with the help of which that body is able to overcome the downward pull by the earth and can escape the earth forever.
OR
The minimum velocity with which an object should be projected from the surface of any planet, so that it escapes from the gravitational influence of the planet.
- Generally, when an object is thrown vertically upward from the earth’s surface, its velocity goes on decreasing and after some time the body falls back to the ground.
- If its initial velocity is increased, the maximum height attained by it is more, but it does fall back to the ground.
- If the initial velocity is increased continuously, for a particular initial velocity, the body can overcome the earth’s gravitational force and move to infinity and come to rest there.
- This velocity is called the escape velocity.
DERIVATION OF EXPRESSION FOR ESCAPE VELOCITY USING LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY.
Consider an object of mass m moving with initial velocity equal to escape velocity on the surface of the earth.
The kinetic energy is given as –
K.E. = ½ mv2
The potential energy is given as –
P.E. = – GMm/R
Total energy on the object on surface of earth
(E1) = K.E. + P.E.
= ½ mv2 + (- GMm/R) …………. 1
When the object escapes the gravitational force of the earth and comes to an infinite distance from the earth,
The K.E. of the object = 0
The P.E. of the object = -GMm/∞ = 0 ………….. 2
Total energy of the object at infinity
E2 = K.E. + P.E.
= 0
From law of conservation of energy, the total energy is always constant.
Therefore, E1 = E2
½ mv2 esc– GMm/R = 0
v2 esc = 2GM /R ………………… 3
we know the equation for acceleration due to gravity –
g = GM /R2
hence, GM = gR2 ………………… 4
put the value of GM in equation 3
v2 esc = 2gR2/R
= 2gR
Vesc = Ѵ2gR ……………… 5
V = Ѵ2 x 9.8 x 6.4 x 106
= Ѵ19.6 x 6.4 x 106
= Ѵ196 x 64 x 106
= 14 x 8 x 100
= 11200 m/s
= 11200/1000
= 11.2 km/s
Why space travellers experience weightlessness in space
- In space, spacecrafts are moving along the orbit.
- The only force acting on it is the earth’s gravitational force.
- Thus, the object is in free fall.
- The velocity of free fall does not depend on the properties on of object, & is same for all objects in the craft
- Thus, if a traveller releases an object, it will remain stationary & appear to be weightless
Akshata kirpekar Youtube channel link ;https://youtu.be/zV0gwjYePlI?si=2jIp9Gnfv2nJ2PRD