Life Processes 1 Test Answers
Q.1. (A) Choose and write the correct option: (5 Marks)
- Water content of Blood Plasma is ……………… .
- 70%
- 90%
- 65%
- 50%
- In which part of cell, electron transfer chain reaction occurs?
- Cytoplasm
- Mitochondria
- Nucleus
- Golgi body
- Which of the following protein is present in skin?
- Haemoglobin
- Insulin
- Keratin
- Ossein
- In which stage the nuclear membrane completely disappears during nuclear division?
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
- Number of chromosomes in diploid cell ………….. .
- n
- 3n
- n/2
- 2n
Q.1. (B) Answer the following (5Marks)
- Find correlation –
- Carbohydrates: 4 Kcal of energy:: Lipids :……9 Kcal of energy
- Glycolysis: EMP Pathway: : Tricarboxylic acid cycle : ….Krebs cycle
- Name the following:
Three scientists who discovered process of glycolysis.
Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof and Jacob Parnas
- State whether the following statements are true or false. Correct the false statements:
Only food stuff is sufficient for energy production.
False. Only food stuff is not sufficient for energy production, but oxygen is also necessary
- Fill in the blanks and explain the statement:
After complete oxidation of a glucose molecule … number of ATP molecules are formed.
38. In glycolysis, 8 ATP are generated. in Kreb’s cycle, 24 ATP are generated, in intermediate step, 6 ATP are generated. So, total 38 ATP are produced from 1 glucose molecule
Q.2. (A) Give scientific reasons (Any 2) 4 marks
- Fibres are one of the important nutrients
- We cannot digest fibre but they help in the digestion of other substances and egestion of undigested substances.
- Hence, fibres are one of the important nutrients.
- Water is an essential nutrient.
- There is about 65-70% water in our body.
- Each cell contains 70% water weight by weight.
- Blood plasma also contains 90% of water.
- Functioning of cells and thereby whole body gets disturbed even if there is a little loss of water from the body.
- Hence, water is an essential nutrient.
- Krebs cycle is also known as citric acid cycle
- Kreb’s cycle is the second step of aerobic respiration.
- It occures in the mitochondria.
- In this step, the Acetyl part of Acetyl CoA gets completely oxidized and from it, citric acid is formed.
- Kreb’s cycle is also known as critric acid cycle because citric acid is the very first stable product generated, in this cycle.
Q.2. (B) Answer the following (Any 3) 6 Marks
- What would happen if:
- Soil with seeds is submerged under water during germination.
- If the soil is submerged under water during germination, seeds perform anaerobic respiration
b. There is insufficient amount of carbohydrates in body due to exceptional conditions like fasting and hunger.
- If there is insufficient amount of carbohydrates in body due to exceptional conditions like fasting and hunger, then lipids and proteins are used for energy production
- Explain glycolysis
- Process of glycolysis occurs in cytoplasm.
- A molecule of glucose is oxidized step by step in the process and two molecules of each i.e. pyruvic acid, ATP, NADH2 and water are formed.
- Molecules of pyruvic acid formed in this process are converted into molecules of Acetyl – Coenzyme A.
- Two molecules of NADH2 and two molecules of CO2 are released during this process.
- Distinguish between : Anaphase and Telophase
- Complete the chart
Mitosis
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
- Observe the figure and answer the following questions.
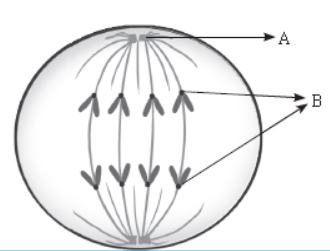
(a) Label the parts A and B.
(A) Centriole (B) Chromatids
(b) Identify the phase of cellular division.
The phase is Anaphase of mitosis cell division.
(c) What phase comes before this phase?
Metaphase is before this phase.
(d) Define the term Karyokinesis.
Karyokinesis means division of the nucleus.
Q.3. Answer the following questions (Any 5) 15 marks
- Explain the Metaphase and Telophase of Mitosis.
Metaphase :
- Nuclear membrane completely disappears. Chromosomes complete their condensation and become clearly visible.
- All chromosomes are arranged parallel to equatorial plane (central plane) of the cell.
- Special type of flexible protein fibres (spindle fibres) are formed between centrioles and centromere of each chromosome
- The chromosomes which have reached at opposite poles of the cell now start to decondense due to which they again become thread like thin and invisible.
Telophase
- Nuclear membrane is formed around each set of chromosomes reached at poles.
- Thus two daughter nuclei are formed in a cell.
- Nucleolus also appears in each daughter nucleus. Spindle fibres completely disappear.
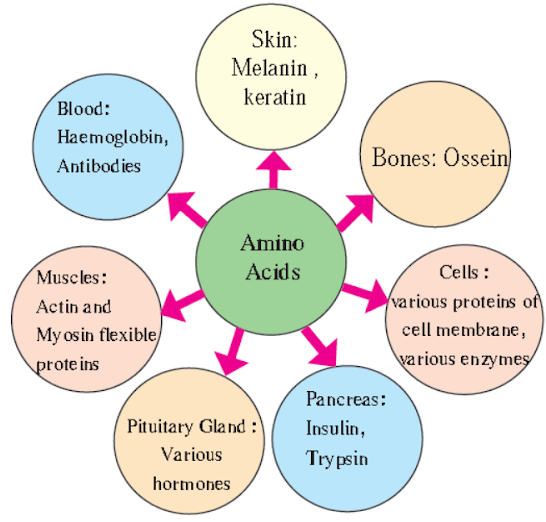
- What are proteins? What is their role in our body?
- Proteins are the macromolecules formed by bonding together many amino acids. Proteins of animal origin are called as first class proteins.
Role of proteins –
- We get 4 kcal of energy per gram of proteins.
- Amino acids are obtained after digestion of proteins.
- These amino acids are absorbed in the body and transported upto each organ and cell via blood.
- From these amino acids, organs and cells produce various proteins necessary for themselves and the whole body.
- Melanin, Keratin, Ossein, hemoglobin, etc
- How are the various processes occurring in the human body controlled? In how many ways?
- The nervous system and the endocrine system bring about control by nervous and chemical coordination in the body.
- Nervous control is brought about with the help of brain, spinal cord and nerves.
- Chemical control is brought about with the help of chemical substances called hormones.
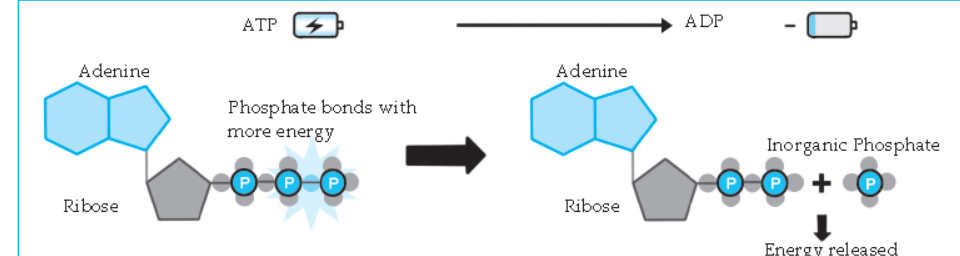
- Explain with the help of a diagram – ATP is called as the energy currency of the cell.
- ATP (Adenosine Tri-phosphate) is an energy rich molecule.
- Energy is stored in the bonds by which phosphate groups are attached to each other.
- As per energy need, energy is derived by breaking the phosphate bond of ATP.
- Hence, ATP is called as the energy currency of the cell.
5. Answer the following
a. Name the processes A and B.
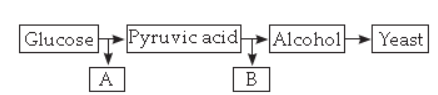
A – Glycolysis
B – Fermentation
b. What type of energy production is shown above?
Anaerobic energy production.
c. Give one point of difference between yeast cells and muscle cells in relation to the above process
In yeast cell, the end product is alcohol and in muscle cells, the end product is Lactic acid.
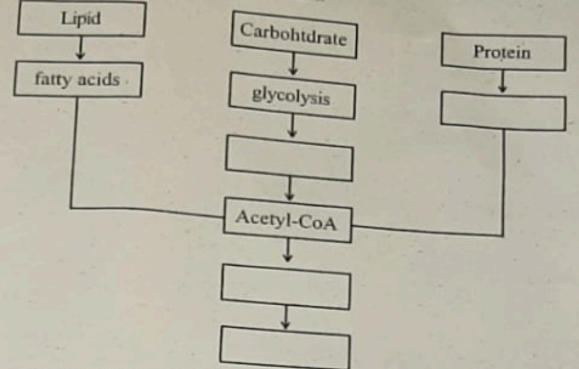
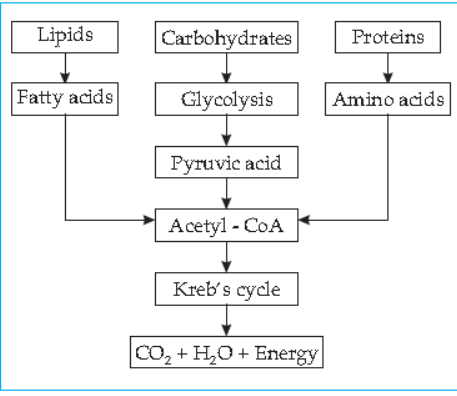
- Complete the chart.
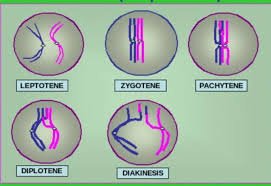
- With the help of suitable diagrams, explain the five stages of prophase I of meiosis
Prophase 1 occurs in following stages –
- Leptotene – Chromosomes become visible and start condensation
- Zygotene – Chromosomes begin pairing and form bivalents
- Pachytene – Crossing over of non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes takes place
- Diplotene – homologous chromosomes of the bivalents separate except at the point of crossing over. They look like X –shaped structures called chiasmata
- Diakinesis – Spindle fibres originate and chromosomes start separate Nucleolus disappears
- Complete the following diagram
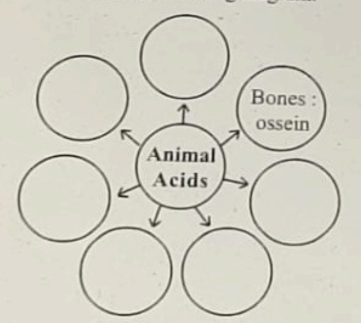
Q.4. Answer in detail:
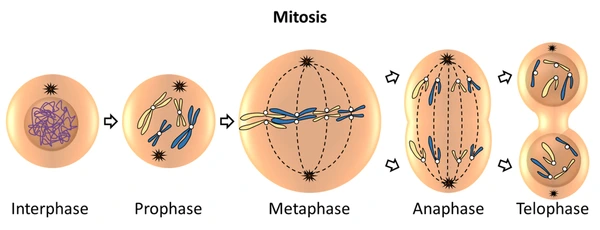
(1) With the help of suitable diagrams explain the mitosis in detail.
This is a type of cell division in which a cell divides to form two identical daughter cells which are identical to the parent cell.
It is completed in two steps – karyokinesis and cytokinesis.
Karyokinesis is nuclear division which is sub-divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase
Cytokinesis is division of cytoplasm.
- Karyokinesis:
Completed in 4 steps:
1. Prophase:
Thread like chromosomes (Chromatin fibres) begin to condense.
Chromosomes become short and thick
Formation of sister chromatids.
Centrioles duplicate and move to opposite poles.
Nuclear membrane and nucleolus start to disappear.
2. Metaphase:
Nuclear membrane completely disappears.
Chromosomal condensation completes.
Chromosomes are clearly visible along with sister chromatids.
Chromosomes are arranged parallel to equatorial plane of cell.
Spindle fibres are formed between centromere and both centrioles.
3. Anaphase:
The shortest phase.
Centromeres split and sister chromatids are pulled apart with the help of spindle fibres at opposite ends.
Each set of chromosomes reach at 2 opposite ends.
Chromosome appear like bunch of bananas
4. Telophase:
It is reverse of prophase
Daughter chromosomes begin to decondense. Chromosomes become thread like and start disappearing.
Spindle fibres completely disappear.
Two daughter nuclei formed
Reappearance of nuclear membrane and nucleolus
Cytokinesis:
After karyokinesis, cytoplasm divides and 2 daughter cells are formed.
In plant cell, cell plate is formed then cytokinesis occurs
In animal cell, a notch is developed which gradually deepens and 2 daughter cells are formed.
(2) Describe Anaerobic respiration. Life Processes 1 Test Answers
- The oxidation of glucose in absence of oxygen is called as anaerobic respiration.
- It occurs in some microbes like bacteria, yeast and lower organisms perform anaerobic respiration. Also, human muscle cells perform anaerobic respiration during vigorous muscle activities.
- It occurs in 2 steps – glycolysis and fermentation.
- Glucose is incompletely oxidized to release energy.
- Pyruvic acid produced is converted into other organic acids or alcohol (C2H5OH) it is called fermentation.
- It occurs in presence of certain enzymes like Zymase
- In oxygen deficiency, some plants and animals also perform anaerobic respiration.
- Seed respire anaerobically if soil is submerged in water.
- Muscle cells respire anaerobically during exercise. When we perform rigorous exercise, the muscle cells require more energy but when less energy is supplied, the cells perform anaerobic respiration and produce lactic acid. As a result, we get cramps in our muscles due to accumulation of lactic acid. During rest, the lactic acid is reconverted to pyruvic acid and the cells perform aerobic respiration again.
Life Processes 1 Test Answers
