Effects of Electric Current
Basic Concepts –Electric charge –The physical property of matter that causes matter to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. It can be positive or negative. Symbol – Q Formula – Q = It Conductors and insulators –Conductors – Substances through which charges can easily pass. Insulators – Substances through which charges cannot pass. Electric current –It is the rate of flow of electric charge. i.e., it is the quantity of charge flowing per unit time. Symbol – I Formula – I = Q / t Unit – Ampere (A) Potential Difference – It is the amount of work done to move a unit charge from one point to the other.Symbol – V Formula – V = W / Q Unit – Volt (V) It is the amount of work done to move a unit charge from one point to the Resistance –It is tendency of the conductor to oppose the flow of current. It is the ratio of the potential difference across its ends to the strength of the current flowing through it. Symbol – R Formula – R = V / I Unit – ohm (Ω) Ohm’s law –If physical conditions like temperature, etc. of a conductor are kept unchanged, the strength of the current flowing through it is directly proportional to potential difference across its ends. V= IR, I = V/R, R = V/I |
| IMPORTANT FORMULAE –
1. I = Q/t 2. V = W/Q 3. V = IR, I = V/R, R = V/I 4. W = H = VIt = I2Rt = V2/Rt 5. P = W/t 6. P = VI 7. P = V2/R 8. H = P x t = (VI) x t = I2Rt = V2t/R |
Can you recall (Page 47)1. How do we decide that a given material is a good conductor of electricity or is an insulator?Any material can be considered as good conductor or bad conductor based on value of its resistance. The substances having low resistance are good conductors while materials with high resistance are insulators. 2. Iron is a conductor of electricity, but when we pick up a piece of iron resting on the ground, why don’t we get electric shock?– When potential difference is applied between two ends of any conductor, then it conducts electricity. – Pieces of iron resting are not charged hence, we do not get an electric shock while lifting it. |
Observe and discussion (Page 47) –What do you observe in the following pictures? We can observe the uses and effects of electric current in various equipment’s.
Which effects of electric current do you find?TV, electric fireplace, lamp – heating effect of electric current. Electric doorbell – magnetic effect of electric current.
|
Joules law of heating
Let ‘V’ be the P.D. applied across two terminals of a resistor of resistance ‘R’ by the cell and ‘I’ be the current in time ‘t’, ’Q’ is the charge flowing, then power ‘P’ is given by
P = energy/ time ……………………………….. 1
Energy is the work done by the cell to move charge Q
Energy = V x Q ………………………………… 2
From 1 & 2,
P = VQ/ t
= VI (as Q/t = I) ………………………… 3
The cell provides the energy to the resistor which is converted into heat energy, given by,
H = P x t = V x I x t ………………………………… 4
According to Ohms law,
V= IR ………………………….. 5
H = V²t / R or H = I²Rt
This equation is called joule’s law of heating.
Unit of electric power:
P = V x I = volt x ampere
= 1 V x 1 A
W = 1J / 1S
1 Watt: When one joule of electric work is done in 1 sec, then the power is one watt.
Commercial unit of electric energy: kilowatt.hr (kWh)
1kWh = 3.6 x 10⁶ J
Unit – When 1 kWh electric energy is used, it is termed as 1 unit
Use your brain power (Page 48) –If in the circuit, the resistor is replaced by a motor, in which form will the energy given by the cell get transformed into?The electric motor will convert the energy into mechanical energy. |
Think about it (Page 48)How can we write mechanical power in a manner similar to the electrical power?Electric power is electric work done per unit time, similarly, mechanical power is amount of mechanical work done in unit time. Mechanical power = mechanical work / time
|
Heating effect of electric current:
- When a resistor is connected in an electrical circuit, heat is produced in it due to the current. This is called heating effect.
- James Joule studied the heating effect of electric current.
- Equipments like water boiler, electric bulb, electric furnace, electric iron, electric cooker, electric kettle, electric toaster, fuse, etc. are based on the heating effect of electric current.
- Coil of alloy nichrome is used in electric heater / cooker
Examples of heating effect –
- Electric bulb – It is used to provide light by heating its filament. Its filament is made of Tungsten (MP – 3400°C).Because of the current, this wire gets heated and emits light. The hot wire also radiates heat to a certain extent.
- Fuse –
- It is a safety device in electric circuits.
- It protects circuits and appliances by stopping the flow of excess current.
- If a current larger than specified value flows through the circuit, the temperature of fuse wire increases and it melts and breaks the circuit.
- MCB –
- Miniature circuit breakers (MCB) switches are used in homes.
- When the current in the circuit suddenly increases this switch opens and current stops.
Short circuiting:
- Domestic circuit contains live, neutral and earth wires.
- Potential difference between live and neutral wires is 220V
- Due to fault in electrical appliances or damage in insulating coating, the two wires – live wire and neutral wire come in direct contact with each other, large current flows through them and large heat is produced.
- When any inflammable material comes in contact around the place, it can catch fire.
- Ways to avoid short circuiting –
- Replacing damaged parts
- Using fuse wire.
- Timely checking the quality of electric equipment
Overloading:
- A flow of large amount of current in a circuit, beyond the permissible value of current is called overloading.
- It occurs when many electric appliances of high power rating like AC, Geyser etc. are switched on simultaneously.
- It can be avoided by not connecting many appliances at a time.
Solved Numericals (Page 50)-
A 6 m long wire made from an alloy, nichrome, is shaped into a coil and given for producing heat. It has a resistance of 22 ohms. Can we get more heat if the wire is cut into half of its original length and shaped into a coil? For getting energy, the two ends of the wire are connected to a source with a potential difference of 220V.

Example 2. A cell is connected to a 9 ohm resistance, because of which heat of 400 J is produced per second due to current flowing through it. Obtain the potential difference applied across the resistance

Example 3. An electrical iron uses a power of 1100 W when set to higher temperature. If set to lower temperature, it uses 330 W power. Find out the electric current and the respective resistances for the two settings. The iron is connected to a potential difference of 220 V.

Example 4. An electric tungsten bulb is connected into a home circuit. The home electric supply runs at 220 V potential difference. When switched on, a current of
0.45 A flows through the bulb. What must be power (wattage) of the bulb? If it is kept
on for 10 hours, how many units of electricity will be consumed?
Given –
Potential difference = 220 V
Current = 0.45 A
Find out –
- Power of the bulb
- Units consumed
Formula –
Power (W) = V x I
Solution –
Power (W) = V x I
= 220 x 0.45
= 99 W
We know that 1 unit = 1kWh
Units consumed in 10 h r s = 99 x 10 = 990 W h = 0.99 k W h = 0.99 units
The power of the bulb is 99W and units consumed in 10 h r s are 0.99 units
Magnetic effect of electric current:
- Flow of electric current through a conductor produces magnetic field around it. It is called Magnetic effect of electric current / Electromagnetism
- Discovered by Hans Christian Orsted.
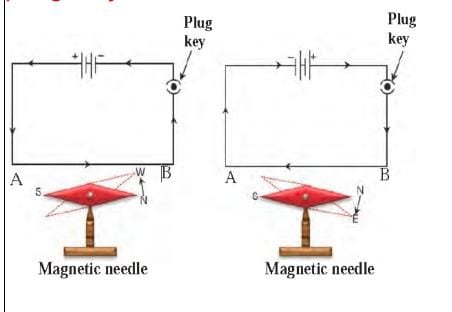
Try this (page 51) –Connect the circuit as shown in figure 4.5. Connect a copper wire, thicker and straight as compared to the connecting wires, between A and B. Keep a magnetic needle adjacent to the wire. Keep the plug key open in the circuit and observe the direction of the needle. Close the plug key and observe the direction of the needle |
Magnetic field due to current carrying conductor
The magnitude of magnetic field produced at a given point is directly proportional to magnitude of current passing through conductor.
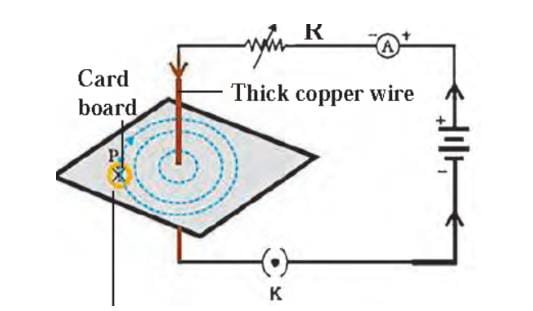
Right hand thumb rule:
Imagine that you are holding current carrying straight conductor in your right hand such that the thumb is held straight and the reimagining fingers are curled around the current carrying conductor then, the thumb points towards the direction of current then the curled fingers around the conductor will give the direction of magnetic field.
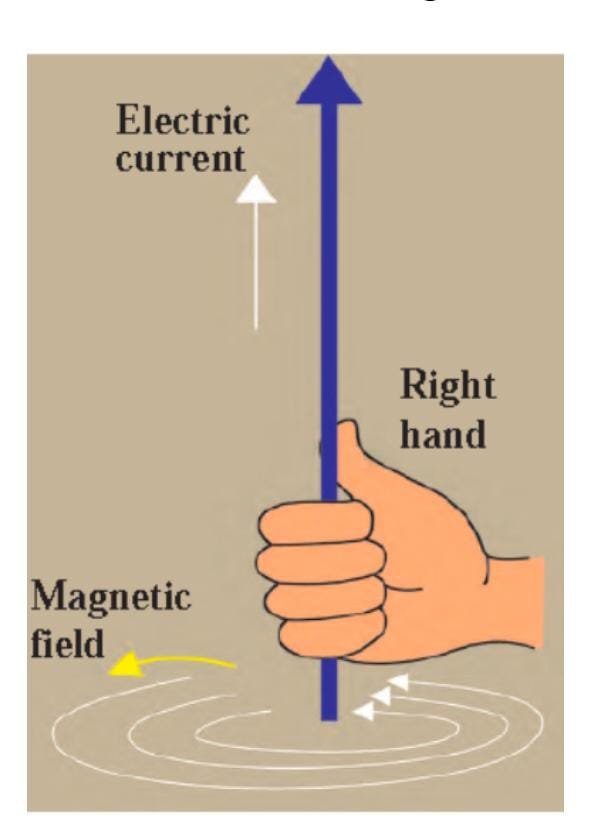
Magnetic field due to a current through a circular loop:
The intensity of magnetic field at any point produced by a current flowing through the wire is dependent on current. It is maximum at the centre of the loop. In the case of circular coil, the magnetic field is proportional to the numbers of turns of the coil.
Effect Of Electric current
Find out(page53)
Magnetic field due to current in a solenoid:
e |
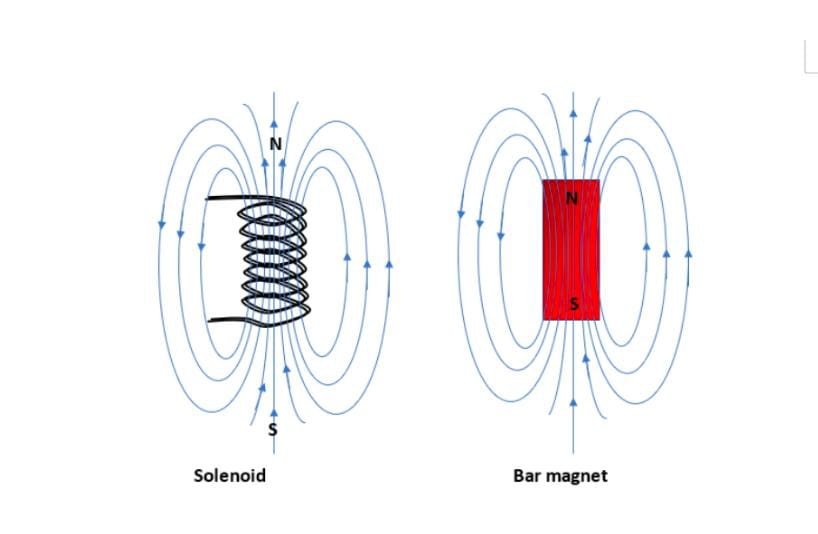
Force on current carrying conductor in magnetic field:
- When current carrying conductor is placed in magnetic field, it is acted upon by force.
- The magnitude of the force depends on current, magnetic field, length of conductor and angle between direction of current and magnetic field.
- The force is maximum when the direction of current is at right angles to magnetic field.
- The force is zero when current and magnetic field have same or opposite directions.
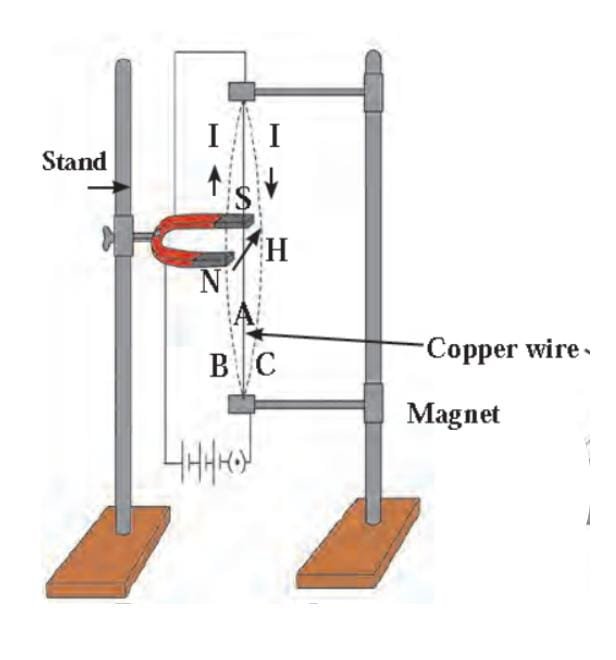
Try this (Page 54) –Materials: Flexible copper wire, stand, electric cell, a horse shoe magnet with a strong magnetic field. Procedure: Using the stand, fix the copper wire so that it passes through the poles of the horse shoe magnet as shown in the figure. Connect the circuit as well.
What do you observe?– When there is no current, the wire remains in a straight line. – When current flows through the circuit, the wire is deflected. – When the direction of the current is from top to bottom the wire comes into position C. – When the direction of the current is from bottom to top the wire comes into the position B.
If the magnet is kept reversed, i.e., its south pole is brought at the position of its north pole and its north pole brought to the position of its south pole, what will happen?When the magnet is kept reversed, the direction of force also gets reversed. The wire is bent in opposite direction. How will you show that the force is maximum when the direction of the current is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field?If the horse shoe magnet in the experiment is moved in some angle, then the force exerted on the copper wire will be less i.e. the wire will show less bending, If the magnet is perpendicular with the wire, the force will be maximum. And the wire will show maximum bending. |
Try this (Page 55) –Determine the direction of the force on the wire in the above experiment and verify your finding.The direction of the force is perpendicular to magnetic field and current. We can verify it using Fleming’s left hand rule. |
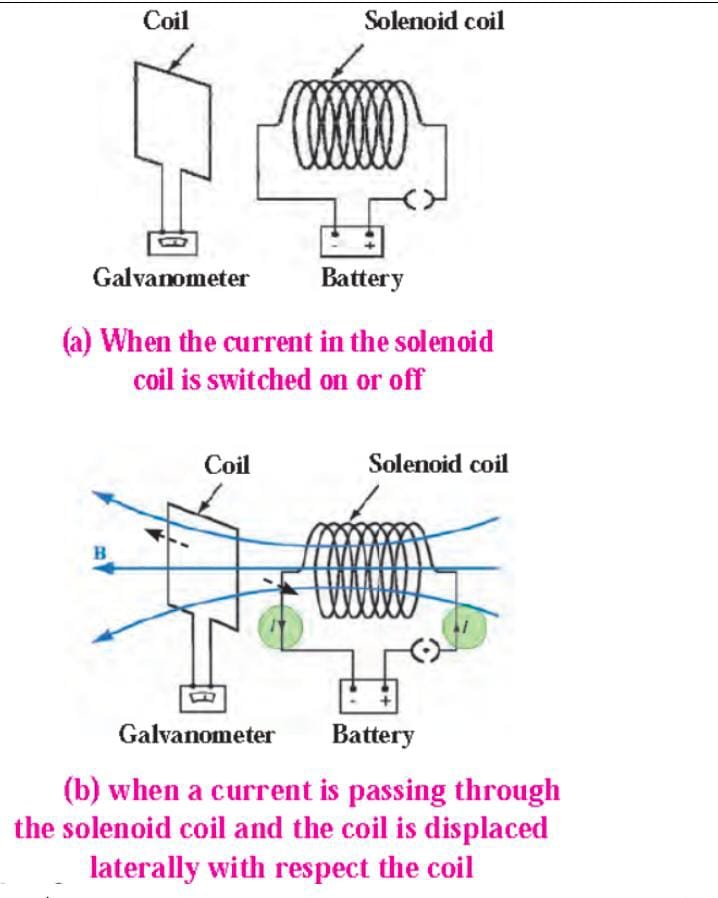
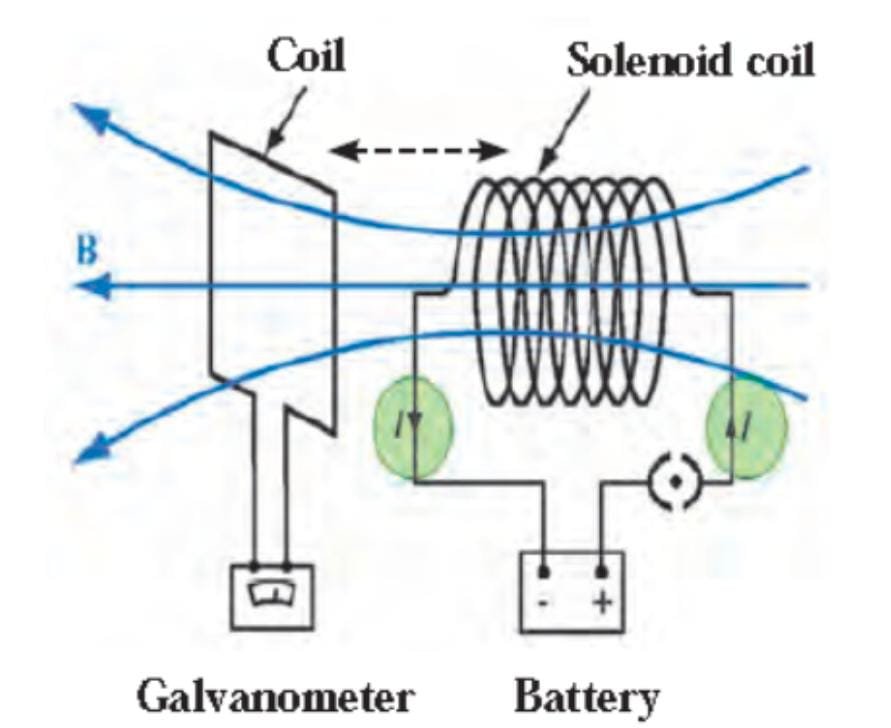
Try this (Page 57) –
a) When the current is switched on, the pointer of galvanometer deflects to a side and comes to zero. When current is switched off, pointer deflects on other side and comes to zero. b) If current is flowing through solenoid coil and the coil is displaced, then current is produced in coil. |
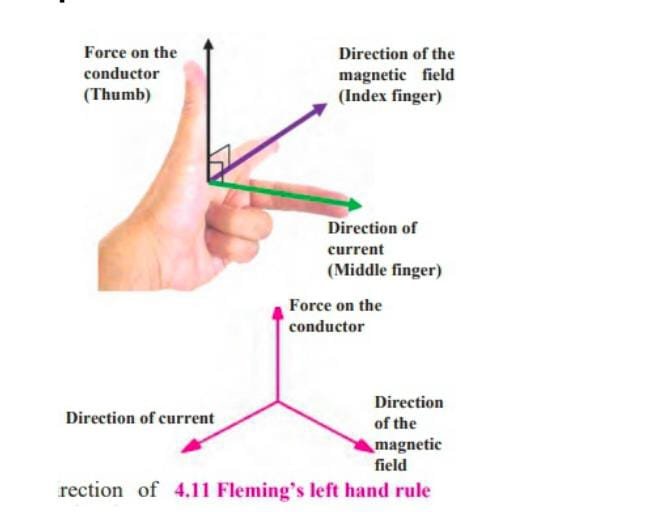
Fleming’s left hand rule:
Stretch the thumb, index finger and middle finger of the left hand so that they are mutually perpendicular to each other. If the index finger is in the direction of magnetic field and the middle finger shows direction of current, then the thumb will point towards direction of force on conductor.
Effect Of Electric current
Electric motor:
It is a device that converts electrical energy to mechanical energy.
Working principle:
Current carrying conductor placed in magnetic field experiences force.
Construction:
1.Rectangular loop:
A large number of turns of insulated copper wire wound on iron core in rectangular shape forms coil ABCD.
2.Strong magnets:
The loop is placed between 2 pole pieces of a strong magnet. Sides AB and CD are perpendicular to magnetic field.
3.Split rings:
It consists of 2 halves of metallic rings R1 and R2. Ends of loop are connected to these rings .The rings are in contact with 2 stationary carbon brushes
4.Brushes:
Two stationary Carbon brushes B1 and B2 are used to press the split rings. The rings rotate between the brushes.
5.Battery:
Supplies current to the armature coil.
6.Axle:
The rings have resistive coating in their inner side and are tightly fitted on the axle. The axle rotates along with the rectangular loop.
Working:
1.When current is passed through the loop, due to the action of magnetic field, according to the Flemings left hand rule, the force is exerted on arm AB in downward direction and on arm CD in upward direction.
2.As the forces are of equal magnitude and opposite in direction, the coil rotates in anticlockwise direction.(A->_B->_C_-> D)
3.After half rotation, the rings R2 and R1 come in contact with brushes B1 and B2 respectively.
4.Current starts flowing in opposite direction(D->C->B ->A)
5.Now the force on arm BA is upward and on DC is downward.
6.This shows that the current in the loop ABCD is reversed after every half rotation and it rotates in same direction.
Electromagnetic induction:
- It is the process by which changing magnetic field in a conductor induces current in another conductor.
- Current can be induced by –
Moving the conductor in magnetic field
Changing magnetic field around it.
- Electromagnetism was invented by Michel faraday
Galvanometer:
- It is a sensitive device used to detect presence of current in circuit.
- It works on the principle that current carrying conductor placed in magnetic field experiences a force
- It has a coil placed between 2 pole pieces of a magnet and a pointer is attached to it.
- When a small current flows through the coil, it will rotate. Its rotation will be proportional to the current.
- The pointer deflects on both sides of zero based on the direction of current.
Effect Of Electric current
Faraday’s law of induction:
- If a current is switched on or off in the solenoid coil, current is induced in the coil.
Law – Whenever the number of magnetic lines of force passing through the solenoid coil changes, current is induced in the coil.
- When a rectangular loop is brought near a solenoid and if a current is switched on or off in the solenoid, current is induced in the loop.
- Also when the current in the solenoid coil is increased or decreased, current is induced in the loop
Effect Of Electric current
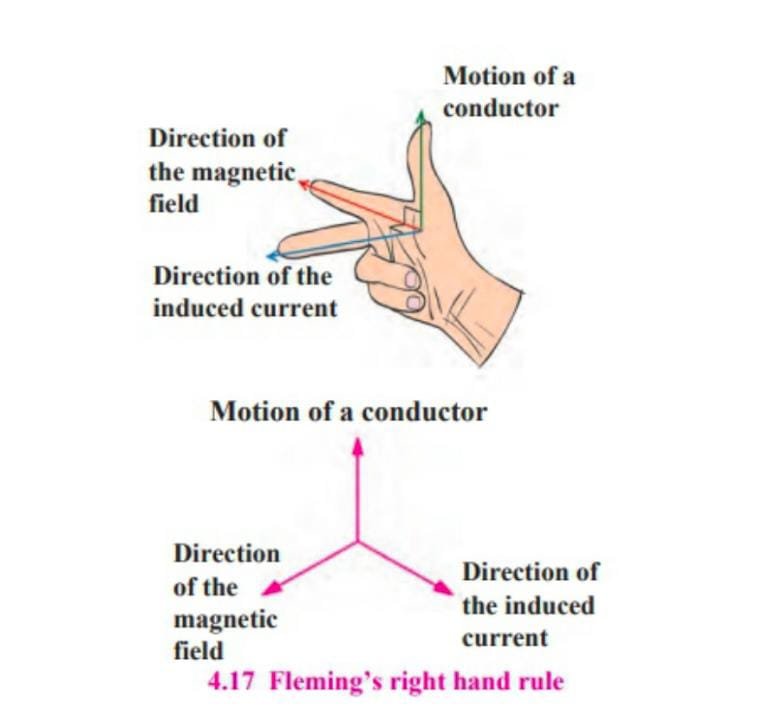
Fleming’s right hand rule –
Stretch the thumb, forefinger and middle finger of the right hand such that they are mutually perpendicular to each other. In this position, the thumb indicates the direction of motion of the conductor, the forefinger indicates the direction of magnetic field, the middle finger indicates the direction of induced current
Effect Of Electric current
Effect Of Electric current
Alternating and direct current –
1.Direct current –
- The current that flows only in one direction is called Direct current.
- It is produced by DC generator
- This current is non oscillatory.
- This current does not change its magnitude.
- This current does not change its direction.
- Voltage of DC cannot travel very far and starts to lose energy.
- Frequency is zero Hz (0 Hz)
- It has limited use
- It is found in batteries, torches, etc.
- 2.Alternating Current –
- The current whose direction reverses periodically with time is called alternating current.
- It is produced by AC generator
- This current is oscillatory.
- This current change its magnitude.
- This current change its direction periodically.
- It is safer to transfer over longer distances as it results into minimum power loss during transmission.
- Frequency is 50 Hz ( 50 cycles / sec)
- It has large scale use
- It is used in electrical household appliances such as electric heater, iron, etc.
- It reaches to maximum then it reduces to zero and increases to maximum in other direction. The oscillations occur in a sinusoidal manner with time.
Effect Of Electric current
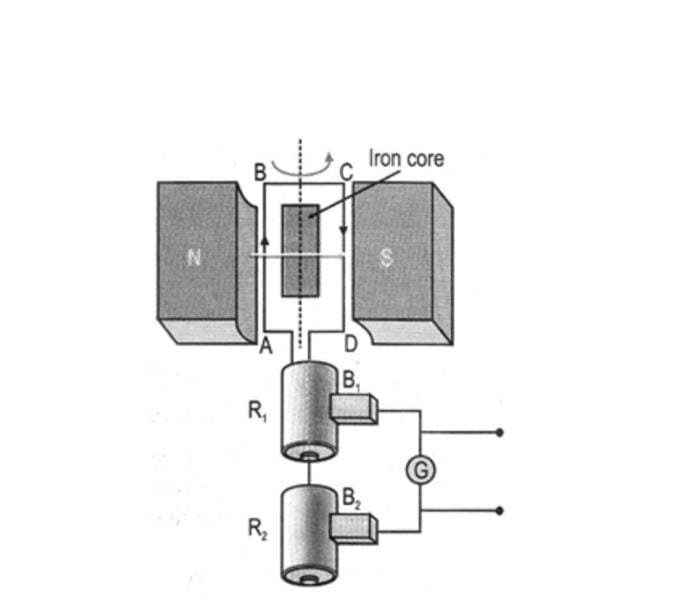
ELECTRIC GENERATOR –
It is a device that converts mechanical energy to electric energy in the form of alternating current.
Principle – It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When the coil of generator rotates in magnetic field, the magnetic field induces current in the coil.
Construction –
1.Rectangular loop:
A large number of turns of insulated copper wire wound on iron core in rectangular shape forms coil ABCD.
2.Strong magnets:
The loop is placed between 2 pole pieces of a strong magnet. Sides AB and CD are perpendicular to magnetic field.
3.Slip rings:
Two ends of loop are connected to two rings R1 and R2 .The rings are in contact with 2 stationary carbon brushes
The rings rotate along with the coil. The rings are fixed to axle
4.Brushes:
Two stationary Carbon brushes B1 and B2 are used to press the slip rings. The rings rotate between the brushes.
5.Axle:
The rings have resistive coating in their inner side and are tightly fitted on the axle. The axle rotates along with the rectangular loop.
6.Galvanometer:
Used to detect the presence of current in the circuit
Effect Of Electric current
Working –
- When the axle is rotated with the help of a machine from outside, the loop ABCD starts rotating.
- On rotating the axle, the branch AB moves upwards and branch CD moves downwards and the loop rotates
- According to Fleming’s right hand rule, the electric current flows in the direction A->B->C->D
- Therefore the current flows from B2 to B1 brush in the external circuit.
- After half rotation, the branch AB and CD exchange their position and the induced current flows in direction D->C->B->A
- The branch BA is always in contact with brush B1 and branch DC is in contact with B2 brush, the current flows from B1 to B2 in external circuit. i.e. in opposite direction.
- This repeats after every half rotation and alternate current is produced
Effect Of Electric current
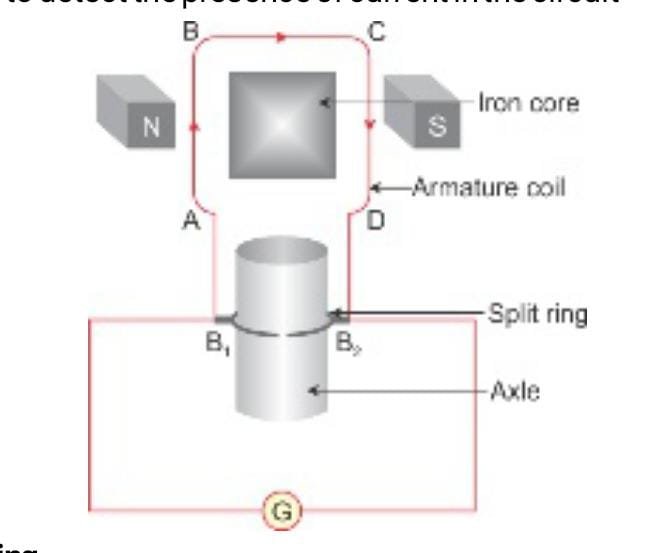
DC GENERATOR –
Construction
1.Rectangular loop:
A large number of turns of insulated copper wire wound on iron core in rectangular shape forms coil ABCD.
2.Strong magnets:
The loop is placed between 2 pole pieces of a strong magnet. Sides AB and CD are perpendicular to magnetic field.
3.Split rings:
Two ends of loop are connected to two rings R1 and R2 .The rings are in contact with 2 stationary carbon brushes
The rings rotate along with the coil. The rings are fixed to axle
4.Brushes:
Two stationary Carbon brushes B1 and B2 are used to press the split rings. The rings rotate between the brushes.
5Axle:
The rings have resistive coating in their inner side and are tightly fitted on the axle. The axle rotates along with the rectangular loop
6.Galvanometer:
Used to detect the presence of current in the circuit
Effect Of Electric current
Working –
- When the axle is rotated with the help of a machine from outside, the loop ABCD starts rotating.
- On rotating the axle, the branch AB moves upwards and branch CD moves downwards and the loop rotates clockwise.
- According to Fleming’s right hand rule, the electric current flows in the direction AàBàCàD.
- Therefore the current flows from B2 to B1 brush in the external circuit.
- After half rotation, the branch AB and CD exchange their position and the induced current flows in direction DàCàBàA
- Since, the branch which is moving upwards is always in contact with brush B1 and the branch which is moving downwards is always in contact with brush B2, current flows in the external circuit.
https://akshatakirpekar.com/?p=25675&preview=true
https://youtu.be/zV0gwjYePlI?si=2jIp9Gnfv2nJ2PRD
Effect Of Electric current