| Can you recall? (Textbook page no. 30)
1. What are the types of molecules of elements and compounds? The molecules of an element are made of one or more atoms that are exactly alike whereas, the molecules of compound are made up of atoms of different types. 2. What is meant by valency of elements? The capacity of an element to combine is called its valency. OR Valency is the number of chemical bonds formed by one atom of an element with other atoms. 3. What is the requirement for writing molecular formulae of different compounds? How are the molecular formulae of the compounds written? The requirements for writing the molecular formulae of compounds are the symbols of the radicals along with their charges (valencies). The molecular formulae of the compounds are written indicating the number of atoms as subscript in the formulae.
|
| Try this (Page 30) –
Apparatus: Thermometer, evaporating dish, tripod stand, funnel, Bunsen burner, etc. Chemicals: Limestone powder, copper sulphate, calcium chloride, potassium chromate, zinc dust, sodium carbonate, phthalic anhydride, etc. Procedure: Carry out the activities 1 to 5 as given below. Read and record the temperatures in the activities 2 to 4. 1. Take a spoonful of limestone powder in an evaporating dish. Heat it strongly on a high blue flame. 2. Add zinc (Zn) dust into the copper sulphate (CuSO4) solution. 3. Add potassium chromate (K2CrO4) solution to barium sulphate (BaSO4) solution. 4. Add sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) solution to the calcium chloride (CaCl2) solution. 5. Take phthalic anhydride in the evaporating dish. On heating, we observe fumes of phthalic anhydride in the inverted funnel. It undergoes sublimation on heating. On cooling, it solidifies on the sides of the funnel in the form of white powder 6. Close the end of the stem of a funnel with a cotton plug. Keep this funnel inverted on the evaporating dish. Heat the evaporating dish on a tripod stand slowly on a low flame. What did you observe in the funnel during heating?
|
Physical change –
- Takes place due to change in temperature, pressure, etc. parameters.
- Composition of matter remains the same.
- Transformation of ice into water.
Chemical change –
- Substances undergo bond breaking and are transformed into new substances by formation of new bonds.
- Composition of matter changes.
- Milk turned into curd.
- The substances taking part in chemical reactions are called
- The substances formed as a result of chemical reaction between the reactants are called
- Chemical reaction is represented by writing chemical equation.
| Physical Change | Chemical Change |
| When a substance undergoes a physical change, its composition remains the same | When a substance undergoes a chemical change, its molecular composition is changed entirely. |
| It is a temporary change. | It is a permanent change. |
| It affects only physical properties i.e., shape, size, etc. | It affects both physical and chemical properties of the substance including its composition |
| It involves very little to no absorption of energy. | During a chemical reaction, absorption and evolution of energy take place. |
| Ex. freezing of water, melting of wax, boiling of water, etc. | Ex. digestion of food, burning of coal, rusting, etc. |
| Here no new substance is formed. | It is always accompanied by one or more new substance(s). |
| These are easily reversible i.e.; original substance can be recovered. | These are irreversible i.e.; original substance cannot be recovered. |
Chemical equations –
- The simple way of representing a chemical reaction in words is called ‘word equation’.
Ex. Hydrogen + Oxygen à Water
- A word equation can be written in a condensed form by using chemical formulae.
Ex. H2 + O2 à H2O
- The representation of a chemical reaction in a condensed form is called a chemical equation.
Writing a chemical equation –
- What are the important conventions followed while writing a chemical equation.
- Reactants are always written on left side
- Products are always written on right side
- Arrow between them indicates direction of reaction
- Plus (+) sign is written between 2 or more reactants / products
- Physical states are mentioned to make the equation more informative.
Solid – s
Liquid – l
Gas – g
Water solution – aq
- Gases are represented as ↑ and precipitate as ↓
- When heat is given from outside then △ is written above the arrow and when heat is released then heat is written along with products
- Conditions like temperature, pressure, catalyst etc are mentioned on arrow
- Special information of reactants and products are written below formulae
- A chemical equation is always written in a balanced form.
|
Try this (Page 33) Apparatus: Test tube, conical flask, balance, etc. Chemicals: Sodium chloride and silver nitrate. Procedure: a) Take sodium chloride solution in a conical flask and silver nitrate solution in a test tube. b) Tie a thread to the test tube and insert it carefully into the conical flask. Make the conical flask airtight by fitting a rubber cork. c) Weigh the conical flask with the help of a balance. d) Now tilt the conical flask and mix the solution present in the test tube with the solution in the conical flask. e) Weigh the conical flask again. Which changes did you find? The solution in the conical flask changes to white colored precipitate. Did any insoluble substance form? Yes, a white insoluble substance is formed. Was there any change in the weight? No, there was no any change in the weight of the flask before and after reaction.
|
DIAGRAM BASED QUESTION –
The reaction of sodium chloride solution with silver nitrate solution is shown in the following figure
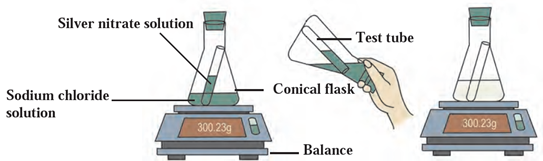
- Name the products of the reaction.
The products are – Silver chloride (AgCl) and Sodium nitrate (NaNO3)
- Write chemical equation involved.
AgNO3(aq)+ NaCl(aq) àAgCl + NaNO3(aq)
- Does the reaction follow law of conservation of mass? Justify your answer.
Yes, the reaction follows law of conservation of mass. There is no change in the weight of the conical flask before and after the reaction
Find out (Pg33)
What are the uses of silver nitrate in everyday life?
- It is used while making photographic films.
- To prepare many silver-based explosives
- Used as an antiseptic in many medical setups.
- Used for the treatment and the removal of unwanted warts in human beings.
Balancing of chemical equation –
- The equation in which the number of elements in the reactants is the same as the number of elements in the products of such an equation is called a balanced equation.
- In any reaction the total mass of elements in the reactants and products is the same
Why we always write a chemical equation in a balanced form?
According to law of conservation of mass, in any chemical reaction, the total mass of each of the elements in the reactants is same as the total mass of each of the respective elements in the products. Hence, a chemical equation is written in a balanced form.
Steps in balancing a chemical reaction –
Balance the following equation –
Sodium hydroxide + sulphuric acid à sodium sulphate + water
Step 1: Write chemical equation from the given word equation
NaOH + H2SO4 à Na2SO4 + H2O ……………… 1
Step 2: Check whether the equation is balanced or not by comparing the number of atoms of the various elements on two sides of the equation.
| Element | Reactants
Number of atoms |
Products
Number of atoms |
| Na | 1 | 2 |
| O | 5 | 5 |
| H | 3 | 2 |
| S | 1 | 11 |
The number of atoms are not same means the equation is unbalanced
Step 3: Start balancing from the compound having maximum number of atoms. Consider that element which has unequal number of atoms on two sides
Here Na2SO4 and H2SO4 Contain maximum number of atoms
Select Na2SO4 for balancing.
Select Na atom as its number is an equal on two sides.
| Number of Na atoms | in reactants
(In NaOH) |
In products (In Na2SO4) |
| Initially | 1
|
2
|
| To balance | 1 x 2 | 2 |
Don’t change the formula of a compound while balancing. instead apply factor 2 to NaOH.
2 NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O …………………………… 2
Check whether the equation is balanced or not.
| Element | Reactants
Number of atoms |
Products
Number of atoms |
| Na | 2 | 2 |
| O | 6 | 5 |
| H | 4 | 2 |
| S | 1 | 1 |
Equation 2 is not balanced at number of O2 and H2 are unequal
First balance H2 as it requires a smaller factor
| No of Atoms of H | In reactants
(NaOH & H2SO4) |
In products (In H2O) |
| Initially | 4 | 2 |
| To balance | 4 | 2 x 2 |
Apply a factor 2 to the product H2O for balancing
2 NaOH + H2SO4 à Na2SO4 + 2 H2O ……………………… 3
Check whether the equation is balanced
| Element | Reactants (LHS)
number of atoms |
Products (RHS)
number of atoms |
| Na | 2 | 2 |
| O | 6 | 6 |
| H | 4 | 4 |
| S | 1 | 1 |
The number of atoms are equal on both sides hence it is balanced.
Step 4: Write down the final balanced equation again
2 NaOH + H2SO4 à Na2SO4 + 2 H2O ……………………………. 4
Types of Chemical Reaction –
| Try this (Pg 35)
Apparatus – Test tube, glass rod, beaker, Bunsen burner, etc. Chemicals: Hydrochloric acid, ammonia solution, magnesium strip, quick lime, etc. Activity 1: Take a small amount of hydrochloric acid in a test tube. Heat the test tube. Dip a glass rod in the ammonia solution and hold on the top of the test tube. You will observe a white smoke emanating from the tip of the glass rod. What must have happened? When hydrochloric acid in the test tube is heated, HCI vapours come out of the test tube. When the glass rod dipped in ammonia is brought near the mouth of the test tube, hydrogen chloride gas and ammonia gas react to form the salt, ammonium chloride in gaseous state. It immediately undergoes condensation process at room temperature and is transformed into the solid state. Hence, a white smoke is observed to be emanating from the tip of the glass rod. NH3(g) + HCl(g) → NH4Cl Ammonia Hydrogen chloride Ammonium chloride Activity 2: Hold a magnesium (Mg) strip in a pair of tongs and ignite. What will you observe? When a magnesium strip is ignited in air, magnesium combines with oxygen from air to form a white powder of magnesium oxide. 2Mg + O2(g) à 2MgO Magnesium Oxygen Magnesium oxide Activity 3: Take water in a beaker up to half of its capacity. Add a few pieces of quick lime (Calcium oxide, CaO) to it. What will you observe? Calcium oxide and water combine to form calcium hydroxide along with the generation of large amount of heat. CaO(s) + H2O → Ca (OH)2(aq) + Heat Calcium oxide Water Calcium hydroxide |
- 1.Combination Reaction:
A + B → AB
The chemical reaction in which two or more reactants combine to give single product is called a combination reaction.
- When Quick lime (calcium oxide) is mixed with water, calcium hydroxide (Slaked lime) is formed.
CaO + H2O → Ca (OH)2 + Heat
- When hydrochloric acid reacts with ammonia, ammonium chloride is formed.
NH3 + HCl → NH4Cl
2. Decomposition:
AB → A + B
The chemical reaction in which two or more products are formed from a single reactant is called ‘decomposition reaction’.
- When sugar is heated, it is decomposed to carbon and water
C12H22O11 → 12C + 11H2O
- Decomposition of Calcium carbonate (Thermal decomposition) – When calcium carbonate is heated, it forms calcium oxide
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
- Hydrogen peroxide decomposes to form water and oxygen
2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2
- Decomposition of Potassium chlorate (Thermal decomposition) – When Potassium chlorate is heated strongly, it forms potassium chloride and oxygen.
2KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2
- Decomposition of ferric hydroxide (Thermal decomposition) – Ferric hydroxide undergoes decomposition to form ferric oxide and water.
2Fe (OH)3 à Fe2O3 + H2O
- Electrolytic decomposition of water –
2H2O electric current 2H2 + O2
- Decomposition of silver chloride –
When silver chloride is kept in sunlight, it decomposes to grey coloured silver
2AgCl sunlight 2Ag + Cl2
Try this (Page 37)
Apparatus: Two test tubes, bent tube, rubber cork, burner, etc.
Chemicals: Calcium carbonate, freshly prepared lime water.
- What will you study using the above apparatus and chemicals?
Using given apparatus and chemicals, decomposition of calcium carbonate and property of evolved gas is studied.
- Draw neat, labelled diagram for the experimental setup.
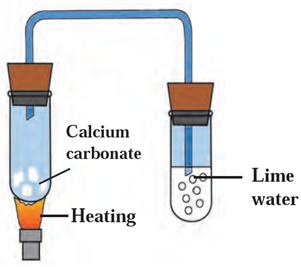
| Try this (Page 37)
Apparatus: Two test tubes, bent tube, rubber cork, burner, etc. Chemicals: Calcium carbonate, freshly prepared lime water. 1. What will you study using the above apparatus and chemicals? Using given apparatus and chemicals, decomposition of calcium carbonate and property of evolved gas is studied. 2. Draw neat labelled diagram for the experimental setup. 3. Name the gas evolved when calcium carbonate is heated. The gas evolved when calcium carbonate is heated is carbon dioxide (CO2). 4. Name the solid product left behind on heating calcium carbonate. The solid product left behind after calcium carbonate is heated is calcium oxide (CaO). 5. What are the products formed when evolved gas reacts with freshly prepared lime water Ca(OH2) The products formed are CaCO3 and H2O
|
How is biogas formed? State its use.
When Organic waste is decomposed by microorganisms, manure and biogas are formed.
Biogas is used as a fuel.
| Can you recall? (Textbook page no. 37)
Is it possible to produce hydrogen by decomposition of water by means of heat, electricity or light? – It is not possible to produce hydrogen by decomposition of pure water by heat or light energy. – But when a few drops of acid are added to pure water then it is possible to decompose such water by passing electric current through it. – Thus, it is possible to produce hydrogen by decomposition of water by using electricity. This process is known as electrolysis.
|
http://CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS CLASS
- Displacement reaction:
AB + C → BC + A
The chemical reaction in which place of ion of less reactive element in a compound is taken by another more reactive element by formation of its own ions is called displacement reaction.
OR
The chemical reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound.
Ex 1. Copper sulphate reacts with zinc to form zinc sulphate
CuSO4 + Zn → ZnSO4 + Cu + heat
Ex 2. Copper sulphate reacts with magnesium to form magnesium sulphate
CuSO4 + Mg → MgSO4 + Cu
Ex 3. Copper sulphate reacts with Aluminium to form Aluminium sulphate
3CuSO4 + 2Al → Al2(SO4)3 + 3Cu
Ex 4. Copper sulphate reacts with iron to form ferrous sulphate
CuSO4 + Fe → FeSO4 + Cu
Ex 5. Copper sulphate reacts with lead to form lead sulphate
CuSO4 + Pb → PbSO4 + Cu
- Double displacement reaction –
AB + CD à AD + CB
The reaction in which the ions in the reactants are exchanged to form a precipitate is a double displacement reaction.
| Activity page 38
When potassium chromate (K2CrO4) is added into the solution of barium sulphate (BaSO4). 1. What was the colour of the precipitate formed? The colour of precipitate was yellow. 2. Write the name of the precipitate. The name of the precipitate is Barium chromate 3. Write down the balanced equation for this reaction. K2CrO4 + BaSO4 → BaCrO4 ↓ + K2SO4 4. Will you call this reaction a displacement reaction or a double displacement reaction This is double displacement reaction.
|
Ex. 2 When silver nitrate (AgNO3) solution is added to sodium chloride (NaCl) solution, a white precipitate of silver chloride (AgCl) is formed along with sodium nitrate (NaNO3)
AgNO3 + NaCl à AgCl + NaNO3
| Study the following chemical reaction and answer the questions – (March19)
AgNO3 + NaCl à AgCl + NaNO3 a) Identify and write the type of chemical reaction. The type of chemical reaction is double displacement reaction. b) Write the definition of above type of chemical reaction. The reactions in which the ions in the reactants are exchanged to form a precipitate are called double displacement reactions. c) Write the names of reactants and products of above reaction. Reactants: Silver nitrate (AgNO3) and sodium chloride (NaCl). Products: Silver chloride (AgCl) and sodium nitrate (NaNO3).
|
| Arnav dissolves a small amount of ‘A’ to a beaker containing water and observes that the solution temperature increases.
What type of process takes place when ‘A’ is added to water, based on temperature change? What do you think substance ‘A’ is: NaOH or KNO3? Explain. When ‘A’ is added to water, an exothermic process occurs. When NaOH is dissolved in water, there is evolution of heat (i.e., exothermic process). When KNO3 is dissolved in water, there is absorption of heat (i.e., endothermic process). Hence, substance ‘A’ is NaOH and not KNO3.
|
Endothermic processes:
Processes, in which heat from outside is absorbed.
Ex. melting of ice, dissolution of potassium nitrate in water
Exothermic processes:
Heat is given out during some physical changes.
Ex. formation of ice from water.
Endothermic reactions:
- The chemical reactions, in which heat is absorbed from the surroundings are called endothermic reactions.
- As heat is absorbed, the temperature of the surrounding falls
- When calcium carbonate is given heat, calcium oxide is formed.
CaCO3 +heat → CaO + CO2
KNO3 + H₂O +heat → KNO3(aq)
Exothermic reaction:
- The chemical reactions in which heat is given away
- The temperature of the surrounding rises as heat is evolved
- When Calcium oxide is mixed with water, calcium hydroxide is formed.
CaO + H₂O → Ca(OH)2 + heat
NaOH + H₂O → NaOH(aq) + heat
| Use your brain power (Textbook page no. 39)
What is the difference in the process of dissolution and a chemical reaction? In the process of dissolution, a chemical substance dissolves in a solvent to form a solution without undergoing chemical reaction. However, a chemical reaction involves chemical change. The chemical composition of the substance changes and a new substance is formed. Does a new substance form when a solute dissolves in a solvent? When a solute dissolves in a solvent, a new substance is not formed.
|
Rate of Chemical reaction-
Factors affecting the rate of a chemical reaction
- a) Nature of the reactant
- The nature or reactivity of reactants influences the rate of reaction
- The more the substance is reactive, the faster is the rate of reaction
- When Aluminum and Zinc react with dilute HCl, Aluminum being more reactive, reacts faster than Zinc
- b) Size of particles of reactants –
- The rate of a reaction depends upon the size of the particles of the reactants taking part in the reaction. Smaller the size of the reactant particles, higher is the rate of the reaction.
- When equal quantities of Shahabad tiles and powdered Shahabad tiles react with dilute HCl, the powdered tiles react faster than pieces and the effervescences of CO2 are formed faster.
- c) Concentration of the reactants –
- Concentrated reactants react faster than dilute reactants
- When equal quantities of dilute and concentrated HCl react with CaCO3, Dilute HCl reacts slowly with CaCO3 and thereby CaCO3 disappears slowly and CO2 also liberates slowly. On the other hand, the reaction with concentrated HCl takes place rapidly and CaCO3 disappears fast.
- d) Temperature of the reaction –
- The rate of reaction increases on increasing the temperature.
- When slaked lime is mixed with water and heated, the lime water forms faster.
- e) Catalyst –
- The substance whose presence increases the speed of reaction without any chemical change in it.
- MnO2 increases the rate of decomposition of potassium chlorate. (KClO3)
- 2KClO3 à 2KCl + 3O2
- MnO2 increases the rate of decomposition of Hydrogen peroxide
| Explain the importance of the rate of chemical reactions in our life
Some chemical reactions occur rapidly while some chemical reactions occur very slowly. The rate at which a chemical reaction occurs is important from biological, economical as well as environmental point of view. Examples: a. Enzymes increase the rate of biological reactions. b. Chemical reactions are profitable in the chemical industries if their rates are fast. c. The depletion or maintenance of the ozone layer depends on the rate of production or destruction of ozone molecules. d. Perishable foodstuffs can be preserved for a longer duration in a refrigerator due to the lower rate of decomposition reaction at low temperature. e. Vegetables cook quickly on oil than on water due to the higher rate of chemical reaction at high temperature. Zinc powder reacts faster than zinc granules when added to copper sulphate (CuSO4) solution. The rate of a chemical reaction depends upon the size of the reactant particles taking part in the reaction. Smaller the size of the reactant particles, faster is the reaction. The size of reactant particles is less in finely powdered zinc as compared to zinc granules. Hence, the reaction with copper sulphate takes place faster with finely powdered zinc than zinc granules. Perishable foodstuffs get preserved longer in the refrigerator. The rate of a chemical reaction depends on temperature. ii. Higher the temperature, faster is the rate of a chemical reaction. The temperature in the refrigerator is low. So, the rate of decomposition of perishable foodstuffs is low and it remains fresh for a longer time. Hence, perishable foodstuffs get preserved longer in refrigerator. Vegetables cook quickly on oil rather than on boiling water. The rate of a chemical reaction depends on temperature. Higher the temperature, faster is the rate of a chemical reaction. The boiling point of oil is higher than that of water. Therefore, when oil is used for cooking vegetables, it provides a higher temperature than water. Hence, vegetables cook quickly on oil rather than on boiling water.
|
Oxidation Reaction –
The chemical reaction in which a reactant combines with oxygen or loses hydrogen to form the product is called Oxidation reaction.
2Mg + O2 à 2MgO (Gain of oxygen)
MgH2 à Mg + H2 (Loss of H2)
Oxidation –
When ferric ion is formed from ferrous ion the positive charge is increased by one unit.
Fe2+ à Fe3+
(Ferrous) à (Ferric)
While this happens, the ferrous ion loses one electron. From this, we understand a new definition of oxidation –
Oxidation means losing one or more electrons.
When the positive charge on an atom or an ion increases or the negative charge on them decreases it is called oxidation
Oxidants / Oxidizing agents –
Chemical substances, which bring about an oxidation reaction by making oxygen available or by itself undergoing reduction, are called oxidants or oxidizing agents.
Examples –
- Acidic potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7/H2SO4)
- Acidic potassium permanganate (KMnO4/H2SO4)
iii. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
- Ozone (O3)
Nascent oxygen is generated by chemical oxidants, and it is used for the oxidation reaction.
O3 à O2 + [O]
H2O2 à H2O + [O]
| Use your brain power (Textbook page 42)
1. Which is the oxidant used for purification of drinking water? Chlorine is used as an oxidant for purification of drinking water 2. Why is potassium permanganate used during cleaning water tanks? It can remove dissolved iron (Fe2+) ions, Manganese (Mn2+) ions and H2S present in water by oxidation reaction. After oxidation, these metals ions aggregate to form solid particles that can be filtered. It also controls growth of bacteria in water storage tank.
|
Reduction Reaction –
The chemical reaction in which a reactant gains hydrogen or loses oxygen to form the product is called reduction reaction.
Ex.1 When hydrogen gas is passed over copper oxide, pinkish brown copper is obtained.
CuO + H2 à Cu + H2O (Gain of H2)
Ex. 2 Ozone decomposes to form oxygen and nascent oxygen.
O3 à O2 + [O] (Loss of Oxygen)
Also, when the positive charge decreases, or the negative charge increases it is called reduction.
Fe3+ + e- à Fe2+
REDOX REACTION –
The chemical reaction in which oxidation and reduction takes place simultaneously, is called redox reaction.
Ex. 1) When hydrogen gas is passed over copper oxide, pinkish brown copper is obtained.
oxidation
CuO + H2 à Cu + H2O
Reduction
In the above reaction reduction of copper oxide takes place and it is converted to copper. Oxidation of hydrogen takes place and water is formed.
Here, CuO is oxidant and hydrogen is reductant.
| The substance which gets oxidized is reductant / reducing agent. The substance which gets reduced is oxidant / oxidizing agent |
2) When barium sulphate reacts with carbon, barium sulphide and carbon monoxide are formed.
Oxidation
BaSO4 + 4C à BaS + 4CO
Reduction
In the above reaction, reduction of Barium sulphate takes place and it is converted to Barium sulphide. Oxidation of carbon takes place and carbon monoxide is formed.
Here, barium sulphate is oxidant and carbon is reductant.
3) When hydrogen sulphide reacts with sulphur dioxide, sulphur and water are formed.
oxidation
2H2S + SO2 à 3S +2H2O
Reduction
In the above reaction, reduction of sulphur dioxide takes place and it is converted to sulphur. Oxidation of hydrogen sulphide takes place and water is formed.
Here, Sulphur dioxide is oxidant and hydrogen sulphide is reductant
CORROSION –
Due to various components of atmosphere, oxidation of metals takes place, resulting in their damage. This is called corrosion.
Ex. Iron gets covered by a reddish-brown layer (rust) when exposed to atmosphere.
4Fe +3O2 +H2O à 2Fe2O3.xH2O
Corrosion of Iron –
When colour coating on some part of metal surface gets removed, the entire structure behaves as an electrochemical cell.
The part from which colour coating is removed, acts as anode (+ve electrode) and the coloured part acts as cathode (-ve electrode)
The reactions at cathode and anode are as follows –
At anode –
As the colour / coating is removed, the metal comes in direct contact with air and undergoes oxidation.
Iron donates electron
| Anode reaction – Fe2+ à Fe3+ + e– |
At cathode –
Reduction reaction takes place at cathode.
Water molecule reacts with CO2 in air to form carbonic acid.
H2O + CO2 à H2CO3
The carbonic acid is very unstable and undergoes decomposition to form H+ ion.
H2CO3 à 2H+ + CO3– –
This H+ accepts electron to form H atom.
H+ + e– à H
This Hydrogen atom reacts with Oxygen to form water
4H + O2 à 2H2O
| Net cathode reaction –
4H + O2 à 2H2O + 4H+ + 4e– à 4H 4H+ + 4e– + O2 à 2H2O |
Net reaction = reaction at cathode + reaction at anode
= 4Fe2+ à 4Fe3+ + 4e–
+ 4H+ + 4e– + O2 à 2H2O
4H++ O2 + 4Fe2+ à 2H2O + 4Fe3+
The water and Fe3+ react with each other to form the rust.
2Fe3+ + 4H2O à Fe2O3.H2O + 6H+
Rancidity:
Fats and oils in food, if kept for a long time, get oxidized and their taste smell changes, it is called rancidity.
Prevention of rancidity-
- Use of antioxidants.
- Storing food in air tight containers.
- Refrigerating food
- Replacing oxygen in the containers with another gas like nitrogen
- Using preservatives like oil, salt, sugar, etc.
- Keeping food away from light
