CELL BIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
Can you recall (Page 88) –What is cell?It is the basic structural and functional unit of life. What is tissue? Which are the functions of tissue?A group of cells having same origin, same structure and same function is called tissue. Animal tissues –
Plant tissues –
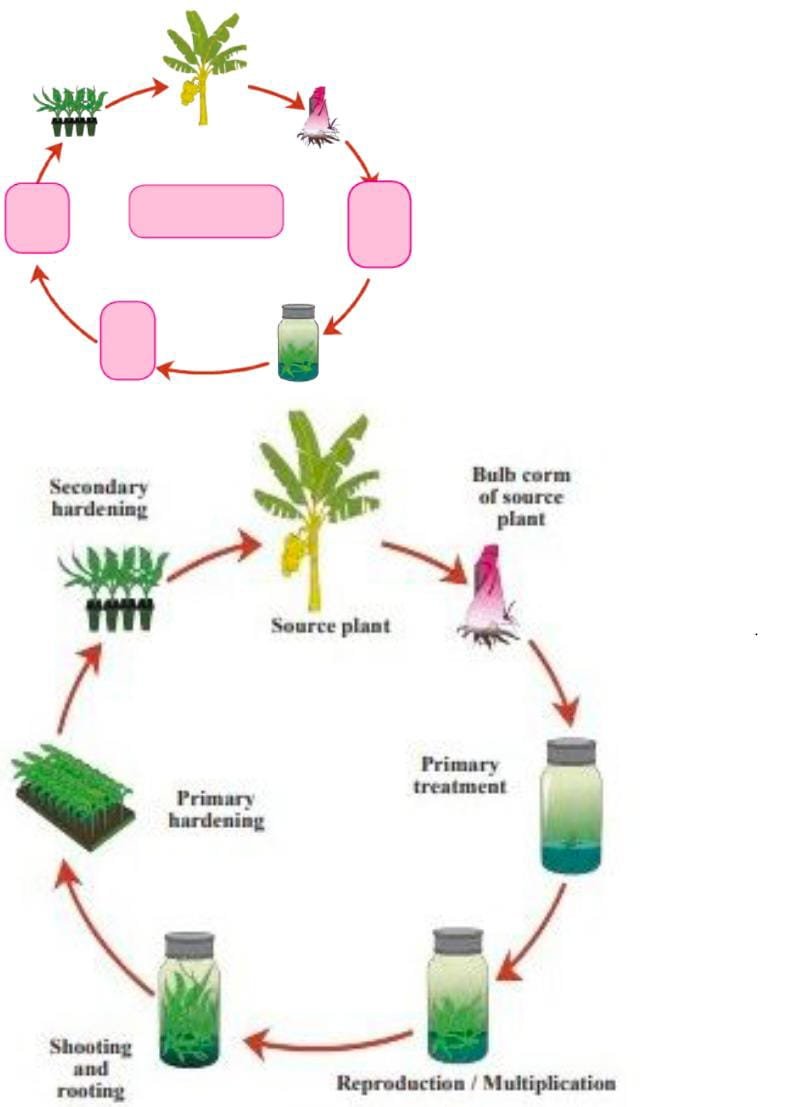
Which technique in relation to tissues have you studied in earlier classes?We have studied techniques like tissue culture. Which are the various processes in tissue culture?Various processes involve primary treatment, primary hardening and secondary hardening. |
CELL BIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
Observe (Page 88) –Assign names to the given diagram.
– Tissue culture is ‘ex vivo’ growth of tissues or cells in a nutrient rich medium. – By using this technique, a complete organism can be developed from a single cell. – A gel like agar medium supplies nutrients for growth. – Improved varieties of plants can be produced. – Various stages in tissue culture are – primary treatment, reproduction / multiplication, shooting and rooting, primary and secondary hardening. |
CELL BIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
Cytology –
Study of structure, types and organelles of cells is called cell biology / cytology.
Stem cells –
- Special types of cells that can give rise to all other types of cells present in the body of as multicellular organism.
- Also play important role in wound healing.
- At the earliest stage of development, organism is in the form of mass of cells & are almost alike. These are stem cells.
- During development, there cells form any type of cell &perform different functions in the body. It is called differentiation of stem cells
- Stern cells are present for longer duration in umbilical cord, blastocyst stage of embryonic development, red bone marrow, and adipose connective tissue.
Preservation of stem cells.
Collected samples are kept in small, sterile vials and are kept in liquid nitrogen at -135°C to -190°C
Types –
1) Embryonic stem cells-
- Cells of embryo undergo repeated mitotic divisions.
- The cell differentiation (Cell take individual characteristics and reach mature / specialized form and function) starts from 14th day of conception.
- Embryonic cells before differentiation are called as embryonic stem cells.
- They can form 220 different types of cells.
- These are parent cells of all types of human cells with self-multiplying ability.
- This ability of stem cells is called
- The stem cells when cultured in laboratory and given biochemical stimulus, they can transform in to desired type of cells.
Totipotent –Source – 4 celled embryo (Up to day 3) The cells have ability to produce all types of cells of developing organism. (Both embryonic and extra embryonic parts like placenta) Pluripotent – Source – Blastocyst, umbilical cord (Embryonic stem cells – 5 to 6 day old embryo) The cells can only make cells of the embryo also germ cells and cells from any of the germ layers.Multipotent – Source – Organs. (Adult / somatic stem cells – Foetus, baby and throughout life.) The cells can produce cells within a given germ layer. Ex. Multipotent cells from mesodermal tissue like blood can make all the cells of blood but can’t make cells of different germ layer. |
CELL BIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
2) Adult stem cells.
- Three main sources of stem cells – red bone marrow, adipose connective tissue & blood
- Also obtained from cord blood
Uses of adult stem cells / importance of stem cells in medical science –
CELL BIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
1) Regenerative therapy
a) Cell therapy- to replace dead cells in diabetes, myocardial infarction (Blockage of blood flow to heart muscle), Alzheimer’s disease (destroy memory), Parkinson’s disease (disorder of CNS that affects movement)
b) To produce blood cells in anaemia, thalassemia, leukaemia, etc.
2) Organ transplantation.
- In case of organ failures, they can be produced with the help of stem cells & transplanted.
- Sometimes organs either become less efficient or functionless due to aging, accidents, infections, disorders.
- If the person gets necessary organ, his life can be saved
Problems associated with organ transplantation –
- Factors like blood group, diseases, disorders, age, etc of donor & recipient should be considered during transplantation.
- Availability of donor – a donor may not be available at all times
- Organs like liver, heart, eyes can be donated only after death. (Posthumous donation)
Body donation –
- Many organs are functional for certain period after death.
- Their donation can save the life of needful persons.
- The body can be made available for research in medical studies.
- It is under the control of Transplantation human organ act, 1994
CELL BIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
Recall (Page 91) –
What is biotechnology?The technique of bringing about improvement in living organisms by genetic modification and hybridization for the welfare of human beings. In which various fields, the biotechnology has been useful?1. Agriculture – for production of cash crops, develop high yielding varieties. 2. Medical science – diagnosis of hereditary diseases, organ transplantation, cancer research, etc. 3. Pharmacy – development of various drugs, vaccines. 4. In pollution control, sewage management. What the impact of biotechnology on agriculture and other related fields?– Development of GM crops that have useful characters and can withstand adverse conditions like famines. – GM crops can resist to pests, chemical. Due to this, use of chemical pesticides is reduced. – Increase in nutritive value of crops – Increase in productivity |
CELL BIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
BIOTECHNOLOGY
It is bringing about artificial genetic changes & hybridization in organisms for human welfare.
Branches of science like, cytology, biochemistry, molecular biology & genetic engineering are included in it.
Areas of biotechnology –
- Using microbes for yoghurt production from milk and alcohol from molasses.
- Production of antibiotics & vaccines using cells.
- Using bio-molecules like DNA & proteins in human welfare.
- Development of plants, animals of desired quality by gene manipulation.
- Production of growth hormone using GMO.
- Use of genetic & non-genetic techniques like tissue culture, hybrid seed production etc.
Benefits
- Increased per hectare yield of crops.
- Expenses on disease control have minimized due to development of resistant varieties.
- Increased per annum yield due to development of fast fruit setting varieties.
- Development of stress resistant varieties to withstand variable temperature, water stress, etc.
CELL BIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
COMMERCIAL APPLICATIONS OF BIOTECHNOLOGY –
1) Crop biotechnology
a) Hybrid seeds – Genes of 2 different crops are recombined.
b) Genetically modified crops – Crops developed with desired characters by integrating foreign gene with their genome.
1.BT Cotton:
Gene is obtained from bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis & integrated with gene of cotton. Toxin produced destroys the alimentary canal of ball worm & it dies.
2.BT Brinjal:
Gene is obtained from bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis & integrated with gene of Brinjal. Toxin produced destroys the alimentary canal of pest & it dies.
3.Golden rice.
Developed in 2005
Gene synthesizing vit. A (Beta carotene) is introduced to rice.
It contains 23 times more amount of beta carotene
4.Herbicide tolerant plants-
Herbicides destroy the main crops along with weeds.
Herbicide tolerant plants can tolerate effect of herbicides.
CELL BIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
c) Bio fertilizers
Using these, nitrogen fixation & phosphate solubilisation abilities of plants are improved.
Bacteria like Rhizobium, Azotobacter, Nostoc, Anabaena, & plants like Azolla are used as biofertilizers
2 Animal husbandry
- Methods like artificial insemination & embryo transfer are used
- Improves quantity & quality of animal products.
- Animals with more strength are developed for hard Work
3) Human health.
- Diagnosis & treatment of diseases are important aspects of human health management
- Diagnosis of diseases it can be done within few minutes & hence the treatment can be done earliest.
- Using biotechnology various medicines are prepared for treatment of diseases.
- Earlier, insulin was collected from pancreas of horse. Now a days, human insulin gene has been inserted into genome of bacteria & prepared
- a) Vaccines & vaccination.
- Vaccine is the antigen containing material given to acquire permanent or temporary immunity against a specific pathogen or disease.
- Earlier completely or partially killed pathogens were used as vaccines.
- Nowadays, antigens are produced in laboratory with the help of gene isolated from pathogen & used as vaccine.
- Proteins acting as antigens are injected in pure form instead of injecting killed or semi-killed pathogens.
Benefits– vaccines produced with the help of biotechnology more thermostable & remain active for long duration.
Edible vaccines
- Transgenic potatoes are being produced.
- These potatoes will act against bacteria like Vibrio cholerae, E. coli.
- Consumption of raw potatoes generate immunity against diseases like cholera.
CELL BIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
What would happen if transgenic potatoes are cooked for consumption?Heating at high temperature would decrease the efficiency and effectivity of the vaccine. |
(b) Treatment-
Useful for production of hormones like insulin, somatotropin & blood clotting factors.
c) Interferon-
Group of small sized protein used in treatment of viral diseases are produced by transgenic E. coli.
d) Gene therapy:
Phenylketonuria (PKT) arises due to genetic changes in liver cells (hepatocyte).
It is treated with somatic cell gene therapy.
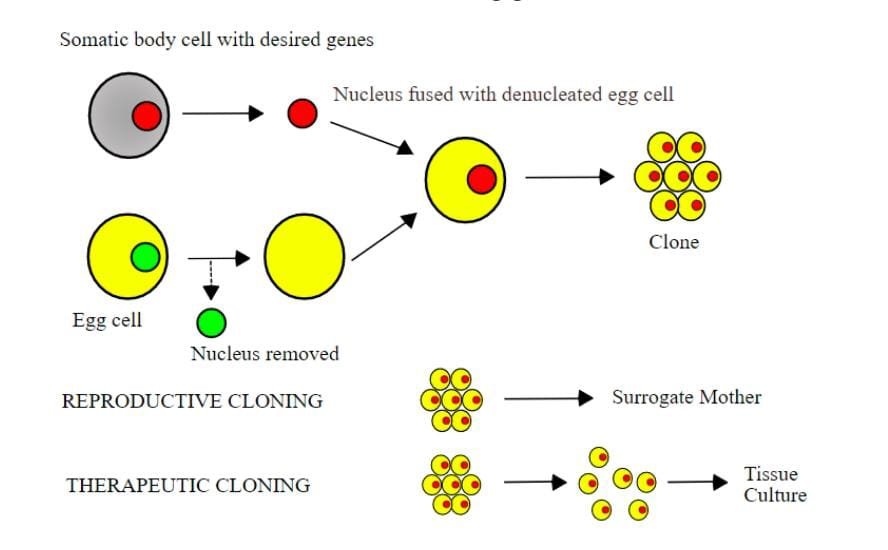
e) Cloning
- It is the production of replica of any cell or organ or entire organism.
- Genes can also be cloned & used for gene therapy & other- purposes.
- Controlling inheritance of hereditary diseases, continuation of generations, enhancing specific tendency etc are possible due to cloning.
(i) Reproductive cloning.
Clone is produced by fusion of nucleus of somatic cell with the enucleated ovum.
No need of sperm to produce new organism.
(ii)Therapeutic cloning.
- Stem cells can be derived from cells formed in laboratory by union of somatic cell nucleus with enucleated egg cell.
CELL BIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
4) Industrial products / white biotechnology
Various products can be produced through less expensive processes
Ex. alcohol production using transgenic yeast.
5) Environment biotechnology
- Sewage should be released in rivers after oxidation with the help of microbial technique.
- Compost is prepared from organic waste by microbes.
- Bio-remediation, bio pesticides, bio fertilizers, biosensors, etc. are used.
Bio-remediation-
It is either absorption or destruction of toxic chemicals and harmful pollutants with the help of plants & microbes.
When plants are used for this purpose, “phyto-remediation”.
Ex.
- Pseudomonas bacteria are used for cleaning the hydrocarbon & oil pollutants from soil and water.
- Fern pteris vitata can absorb arsenic from the soil.
- Genetically modified mustard can absorb selenium from soil.
- Sunflower can absorb uranium & arsenic.
- Bacterium Deinococcus radio durans is used to absorb the radiations from radioactive debris.
(f) Grasses like alfalfa, clover, rye are used in phyto-remediation.
6) Food biotechnology:
Food items like bread, cheese, wine, beer, yoghurt, vinegar are produced.
7) DNA fingerprinting-
- DNA sequence of each person is unique as that of the fingerprints. Identity of any person can be established with the help of available DNA. It is called DNA fingerprinting. It is used in forensic science, identify criminal, identify father of a child.
- Centre for DNA fingerprinting diagnostics, Hyderabad.
GREEN REVOLUTION
- Various methods applied for harvesting maximum yield from minimum land are collectively called as green revolution.
- Norman Borlaug (USA) & Dr. M.S. Swaminathan have valuable contribution in green revolution.
- Improved dwarf varieties of wheat & rice, proper use of fertilizers & pesticides & water mgt. has led to the increased production of food grains
WHITE REVOLUTION
- Verghese Kurien is considered as The father of white revolution.
- He put cooperative movement of Anand Milk, Gujrat.
BLUE REVOLUTION
- Production of various useful aquatic organisms with the help of water is called as blue revolution.
- Government has encouraged people for pisciculture by launching program Nil-Kranti Mission- 2016′ by giving 50-100% subsidies.
- Fresh water fishes- rohu, catla others like shrimp, lobsters, etc. are cultured.
FERTILIZERS
- Two types used are- organic manure & chemical fertilizers.
- Water holding capacity of soil improves due to manures.
- Upper soil layer is formed due to humus formation.
- Earthworms & fungi make available essential elements like N, P, and K to plants.
- Soil less farming (hydroponic) uses liquid chemical fertilizers
INSECTICIDES
- Frogs, insectivorous birds, pesticides are used to control insect
- Pesticides are poisonous that enter the food web the food & water and their bio-magnification occurs.
- DDT, malathion, chloropyriphos, etc.
ORGANIC FARMING
- Continuous use of chemicals have led to problems like- soil infertility, pest infestation, etc.
- Organic forming includes complete ban on chemical Fertilizers & pesticides & use of local, sturdy varieties & maintain natural balance.
APICULTURE –
Artificial bee boxes are used to collect honey without destroying the hives.
FRUIT PROCESSING –
Fruits are perishable agro produce.
They are processed to use them throughout the year.
Various methods of fruit processing – storage in cold storage to drying, salting, air tight packing, preparing murabba, evaporating, etc.
CELL BIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
https://akshatakirpekar.com/?p=25675&preview=true
https://youtu.be/zV0gwjYePlI?si=2jIp9Gnfv2nJ2PRD